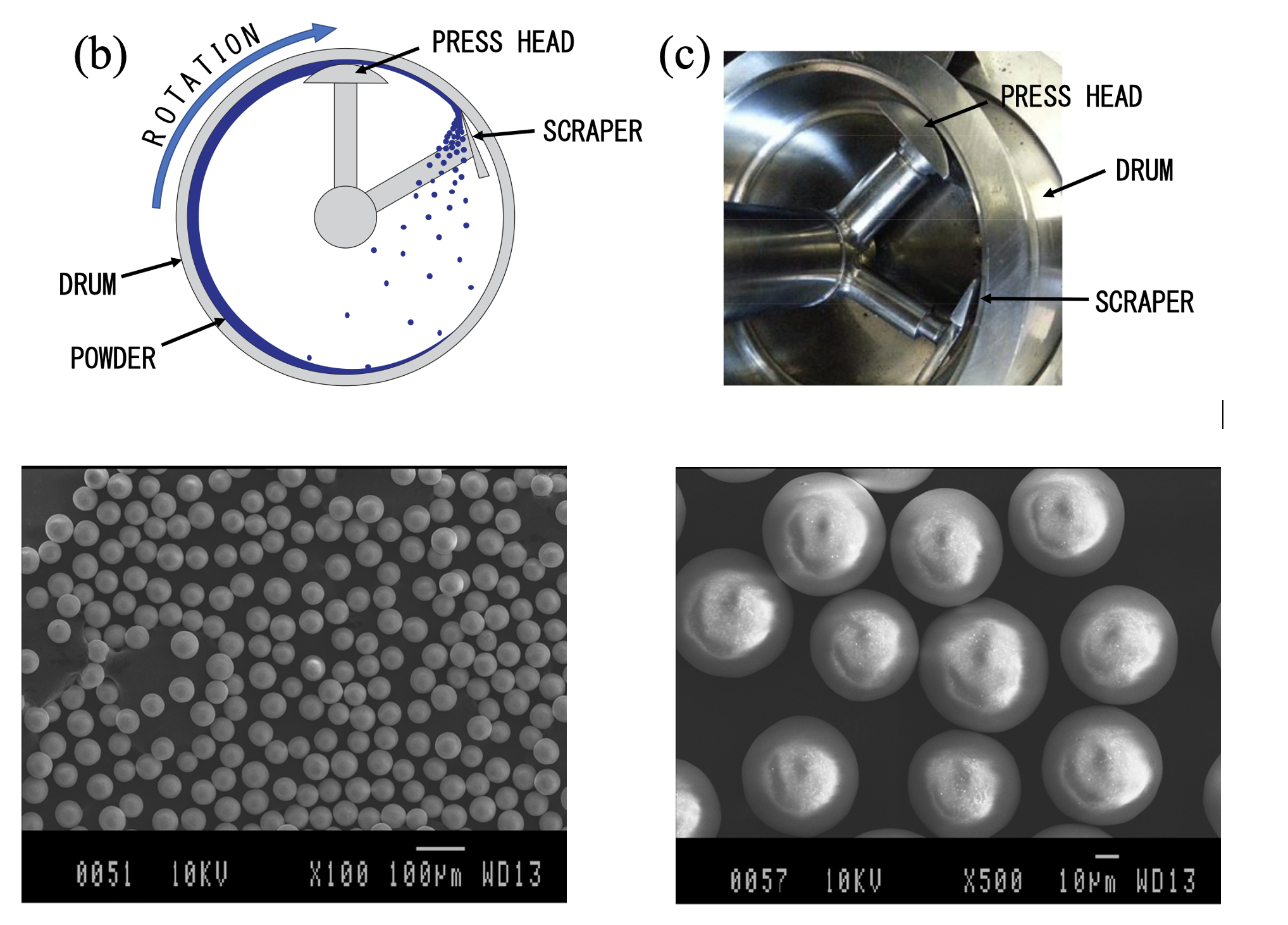
Dry Particle Microgranulation Process
The DPMG method utilizes a mechanofusion method and was discovered in the process of coating different particles. In mechanofusion, particles are introduced into a spinning drum (1,000 – 5,000 rpm). Particles are forced onto the wall of the drum due to the high spinning forces, where they must pass through a small gap between the rotating drum and a stationary press head. The stationary scraper scrapes the powder off the wall. This method is typically used as a spheronization method but be utilized in coating particles. For the synthesis of monodispersed uniform 10 um particles, it was observed that submicron feedstock particles can be aggregated into micron-sized particles by implementing the use of larger template particles, in this case, 50 um ZrO2 spheres were selected shown in the SEM images below.
NMC Particle SynthesisÂ
Using the method described above it is possible to synthesize NMC particles by using oxide feedstock particles in stoichiometric proportions and a Li-source. Oxide feedstock particles are first jar-milled to produce amorphous feedstock particles with submicron grains. The feedstock particles are then combined with the ZrO2 template particles and processed via mechanofusion. The resulting particles are rounded and have an average size of 25 um, when compared with commercial NMC particles shown below. Regarding, waste unlike the CSTR method any waste from the classification process of DPMG could be reprocessed again thus we believe this process can operate at near 100% yield.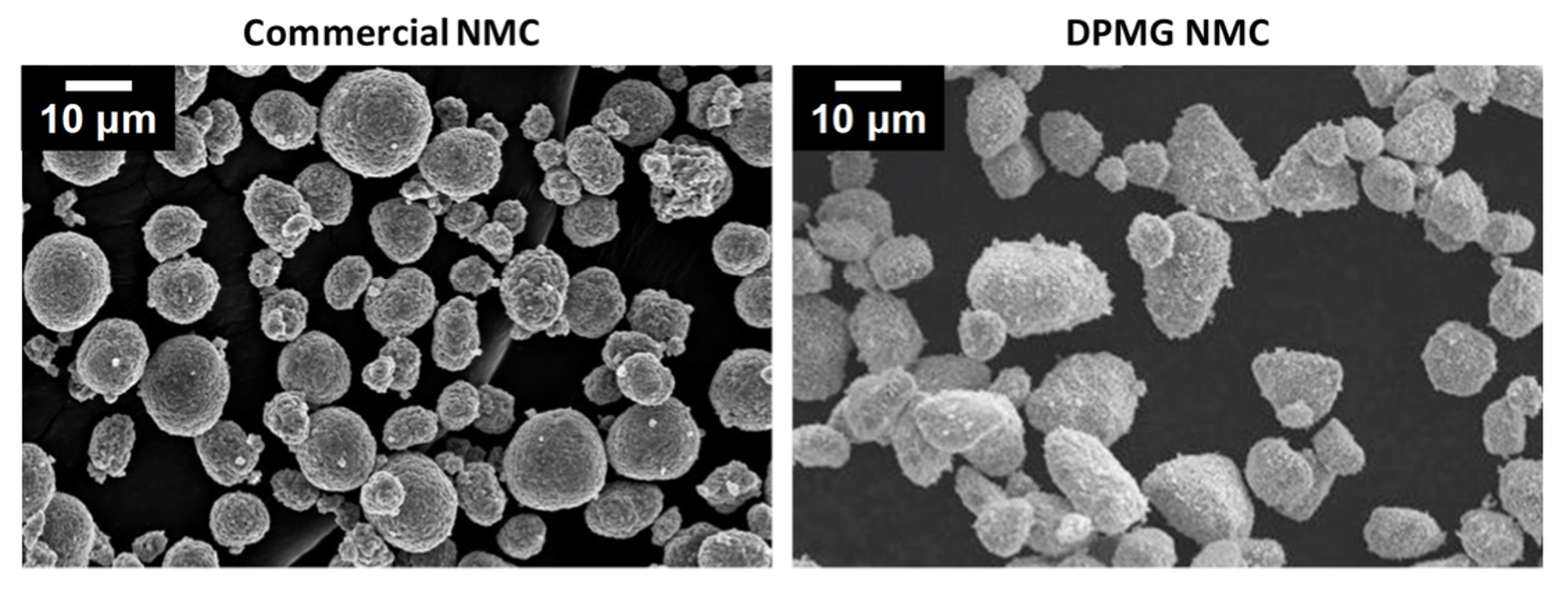 Other classification steps are utilized such as cross-sectional and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) SEM images (Shown image(s) E-H). Highlighting unform element distribution comprising 0.5 um grains and some voids. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) pattern of DPMG NMC111 (Shown image I) indicates phase pure and with high crystallinity. Electrochemical performance of DPMG NMC 111 (Shown image(s) J-K) shows comparable performance to commercial NMC made using CSTR, even though here the particles are not modified with any sort of coatings or dopants.Â
Other classification steps are utilized such as cross-sectional and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) SEM images (Shown image(s) E-H). Highlighting unform element distribution comprising 0.5 um grains and some voids. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) pattern of DPMG NMC111 (Shown image I) indicates phase pure and with high crystallinity. Electrochemical performance of DPMG NMC 111 (Shown image(s) J-K) shows comparable performance to commercial NMC made using CSTR, even though here the particles are not modified with any sort of coatings or dopants. 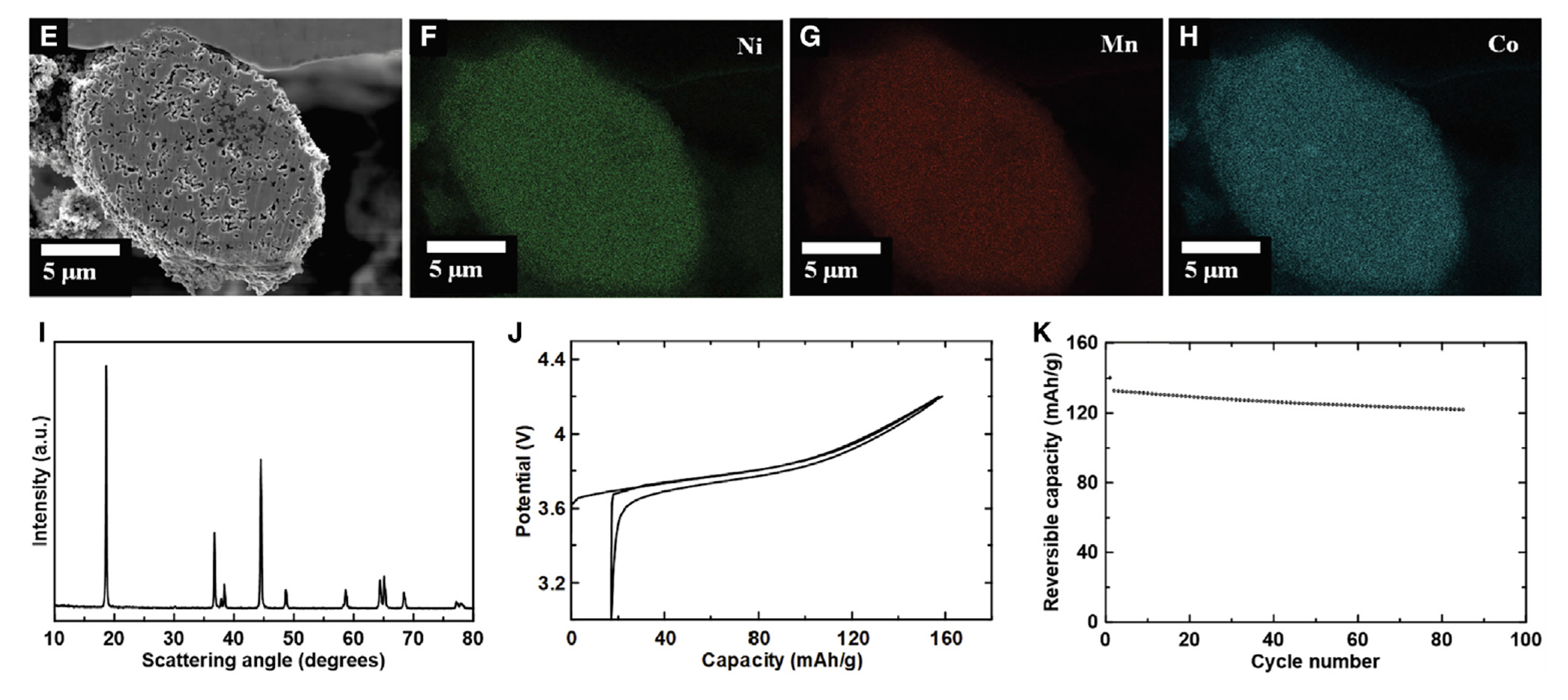
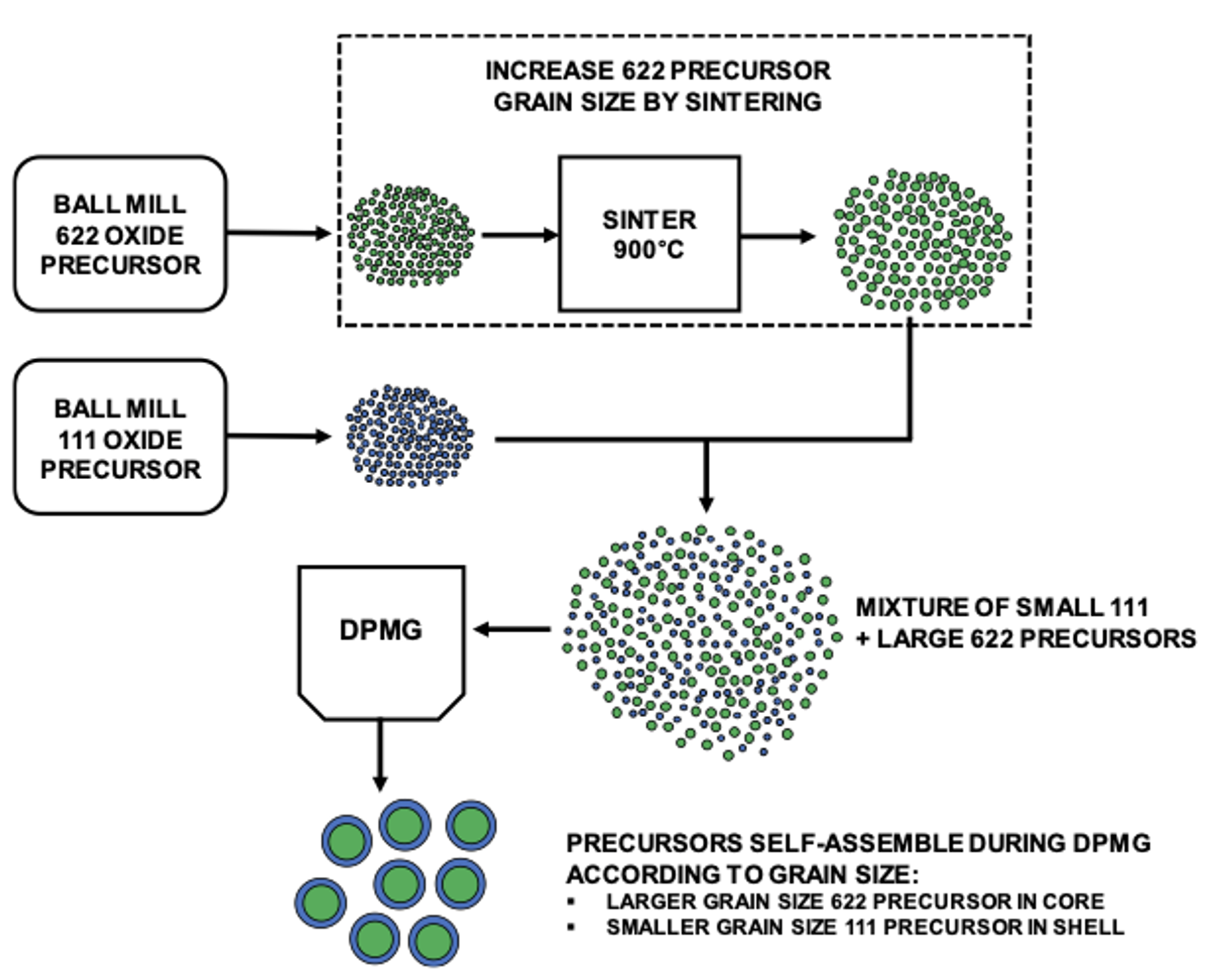
Core-Shell NMC Particle Synthesis
As a proof of concept, the NMC particles with a Ni-rich core and an Mn-rich shell were synthesized shown in the schematic below:Â
Cross-section SEM images were taken at low magnification was taken (Left) which shows that larger Ni-rich precursor particles and the smaller Mn-rich precursor particles are well segregated in the core and shell respectively. An SEM image of the particle following high-temperature sintering, SEM image (Right) illustrates the formation of a concentration-gradient particle. Future publications will outline the details of synthesis, structure and electrochemistry of core-shell particles using the DPMG method. 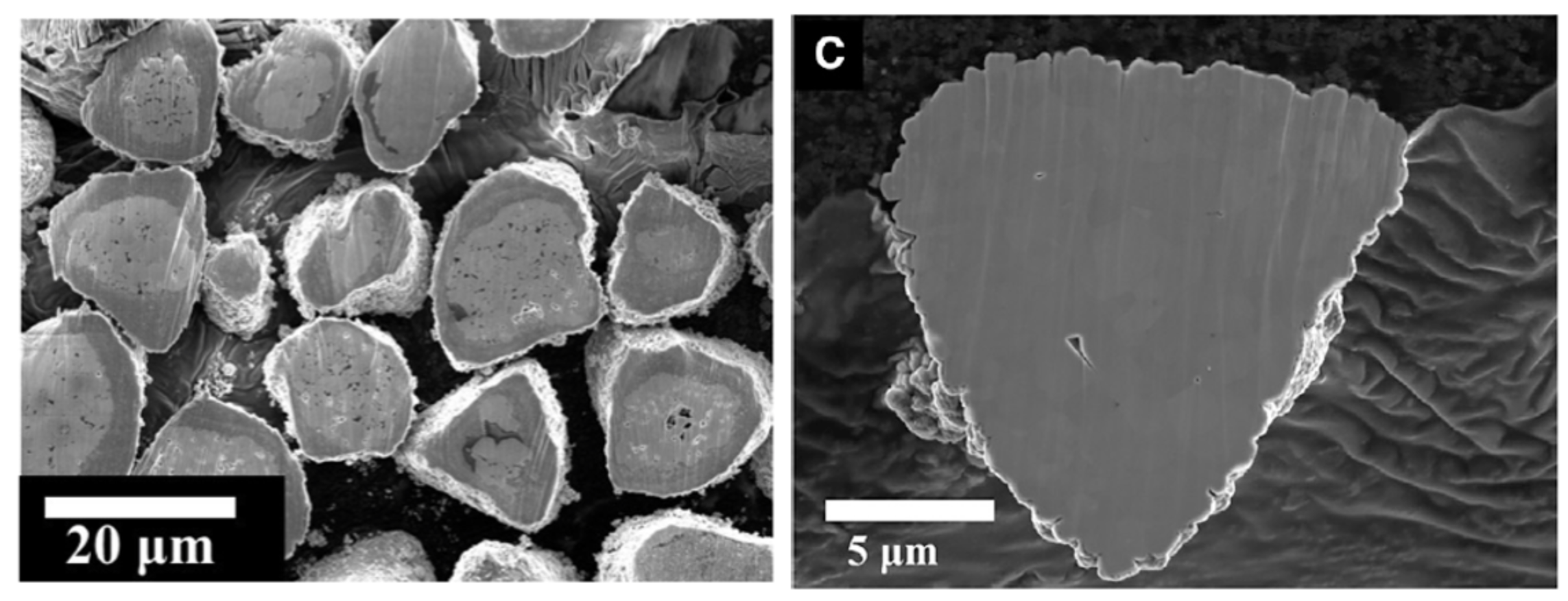
To summarize, the DPMG method is described as a new low-cost and environmentally friendly method to produce complex powder particles with no waste and at 100% yields. We believe that this method will lead to significant cost-saving measures in engineered powdered particle synthesis and enable the synthesis of new materials with precise control of particle morphology. For more information please
